Astronomy Which Wavelength Use to See Protostars Easily
During this time and up until hydrogen burning begins and it joins the main sequence the object is known as a protostar. Protostars viewed nearly pole-on will have bluer and more intense radiation than those viewed nearly in the plane of the disk.

Esa S Xmm Newton Reveals Missing Intergalactic Material Dark Energy Dark Matter Galaxies
The dust and gas that surround the formation of a new star block light making it hard to see any visible light.

. Located at a distance of 2450 light-years the globule is a condensation of dense gas that is barely surviving the strong ionizing radiation from a nearby massive star. C 40000 astronomical units. C 40000 astronomical units.
Evolution of the material surrounding protostars has pro-gressed with the availability of medium and high res-olution spectroscopic instrumentation at near and mid-infrared wavelengths 2 - 20zm. The wavelength of infrared light ranges from 075 to 300 micrometers and falls in between visible radiation which ranges from 380 to 750 nanometers and submillimeter waves. Our observations provide a first glimpse at protostars that have just begun to glow at far-infrared wavelengths said Elise Furlan from the National Optical Astronomy.
We have learned a lot about star formation since the invention of detectors sensitive to infrared radiation because infrared radiations are not visible and can only be detected using certain infrared sensitive detectors. At such wavelengths they searched for radio emissions from methanol CH 3 OH wood alcohol not for drinking. In other words far too little matter is accreting onto these protostars at any given time theres simply no way a protostar could become a full-fledged star in just a few million years at.
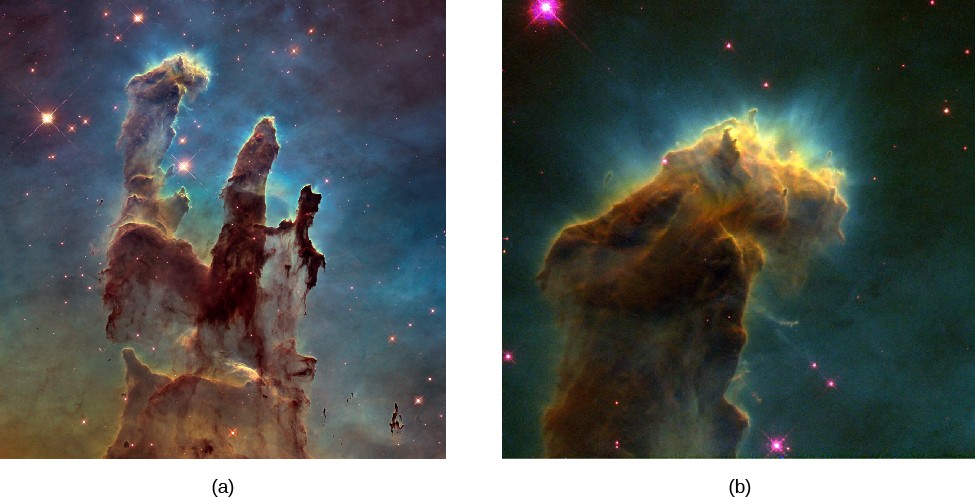
A This Hubble Space Telescope image of the central regions of M16 also known as the Eagle Nebula shows huge columns of cool gas including molecular hydrogen H2 and dustThese columns are of higher density than the surrounding regions and have resisted evaporation by the ultraviolet radiation from a cluster of. Infrared astronomy uses the wavelength range from about 1 micrometer to a few hundred micrometers. Study the graph of the intensity of light versus wavelength for continuous spectra observing how it changes with the temperature of the light bulb.
The typical observed protostar has a spectral energy distribution peaking at 60100 μm although the peak wavelength and the intensity of the radiation will depend on the viewing angle with respect to the rotation axis. Neptune is about 30 astronomical units from the Sun. Lution of the material surrounding protostars has progressed with the availability of medium and high resolution spectro-scopic instrumentation at near and mid-infrared wavelengths 220 m.
E 05 astronomical units. Higher energy shorter wavelength infrared light emitted by stars. Recent observations suggest that T Tauri stars may actually be stars in a middle stage between protostars and hydrogen-fusing stars such as the Sun.
The submillimeter-wavelength glow arising from the cold dust clouds is seen in orange in this image and is overlaid on a view of the region taken in the more familiar visible light. Infrared astronomy began in the 1830s a few. This stage of stellar evolution may last for between 100000 and 10 million years depending on the size of the star being formed.
Wavelengths near 1000 micrometers 1 millimeter are considered radio waves and studied by radio astronomers using different techniques than infrared astronomers. The globule is being compressed by the surrounding. The progress made is best illustrated by the observations of high mass protostars which are bright and easy to observe.
Start studying Astronomy 113 Exam 1. When astronomers actually observe these protostars in action they appear far too faint. The VLA was used to observe a pair of protostars known as IRAS 4A in a star-forming region located nearly 1000 light-years from Earth.
A 40 astronomical units. The astronomers used the VLA to observe a pair of protostars called IRAS 4A in a star-forming region about 1000 light-years from Earth. D 15000 astronomical units.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. An object in the Outer Oort Cloud might be at a distance from the Sun of. The progress made is best illustrated by the ob-servations of high mass protostars which are bright and easy to observe.
The astronomers used the VLA to observe a pair of protostars called IRAS 4A in a star-forming region about 1000 light-years from Earth. Visible lights short tight wavelengths are prone to bouncing off dust particles making it hard for visible light to escape from a dense nebula or protoplanetary cloud of gas and dust. High-resolution infrared images have revealed jets of material as well as stellar winds coming from some T Tauri stars proof of interaction with their environment.
If the final result is a protostar with more than 008 solar masses it will go on to begin. At those wavelengths they sought radio emissions from methanol CH3OH wood alcohol not for drinking. The pair was observed at wavelengths of the order of centimeters.
This light penetrates dusty nebulae allowing us to see into the galactic interior. Figure 212 Pillars of Dust and Dense Globules in M16. Why can we see protostars with infrared telescopes.
We can see the Suns _____ most easily during total solar eclipses. Because the cloud absorbs energy from its central protostar the dust around the protostar becomes heated to a few hundred kelvins which makes it radiate thermal energy at infrared wavelengths causing it to be relatively transparent t tauri stars -eject massive amounts of material into space. They observed the pair at wavelengths of centimeters.
Solution for The wavelength region of the electromagnetic spectrum in which protostars are most easily observable is the a. Infrared astronomy is a sub-discipline of astronomy which specializes in the observation and analysis of astronomical objects using infrared radiation. B 3 astronomical units.
The Elephants Trunk Nebula is an elongated dark globule within the emission nebula IC 1396 in the constellation of Cepheus. The longer wavelengths of infrared light slip past dust more easily and therefore instruments that detect infrared lightlike those on Webbare able to see the objects that emitted that light inside a. Infrared astronomers divide the infrared spectrum into near- mid- and far-infrared.
See theres always been a problem with the previous theory. They observed the pair at wavelengths of centimeters.

Formation Of Stars Excellent Page Star Formation Gravitational Potential Energy Astrophysics

Multi Wavelength Views Of Protostars In Ic 1396
Astronomy Science Quiz Quizizz

Paisajes Increibles On Twitter Astronomy Nebula Astronomy Pictures

Types Of Stars Stellar Classification Lifecycle And Charts Star Classification Stars Temperature Chart

Esa Observations Seeing In Infrared Wavelengths

How The Milky Way Works Milky Way Galaxy Milky Way Spiral Galaxy
Astrobiology Institute At The University Of Hawaii
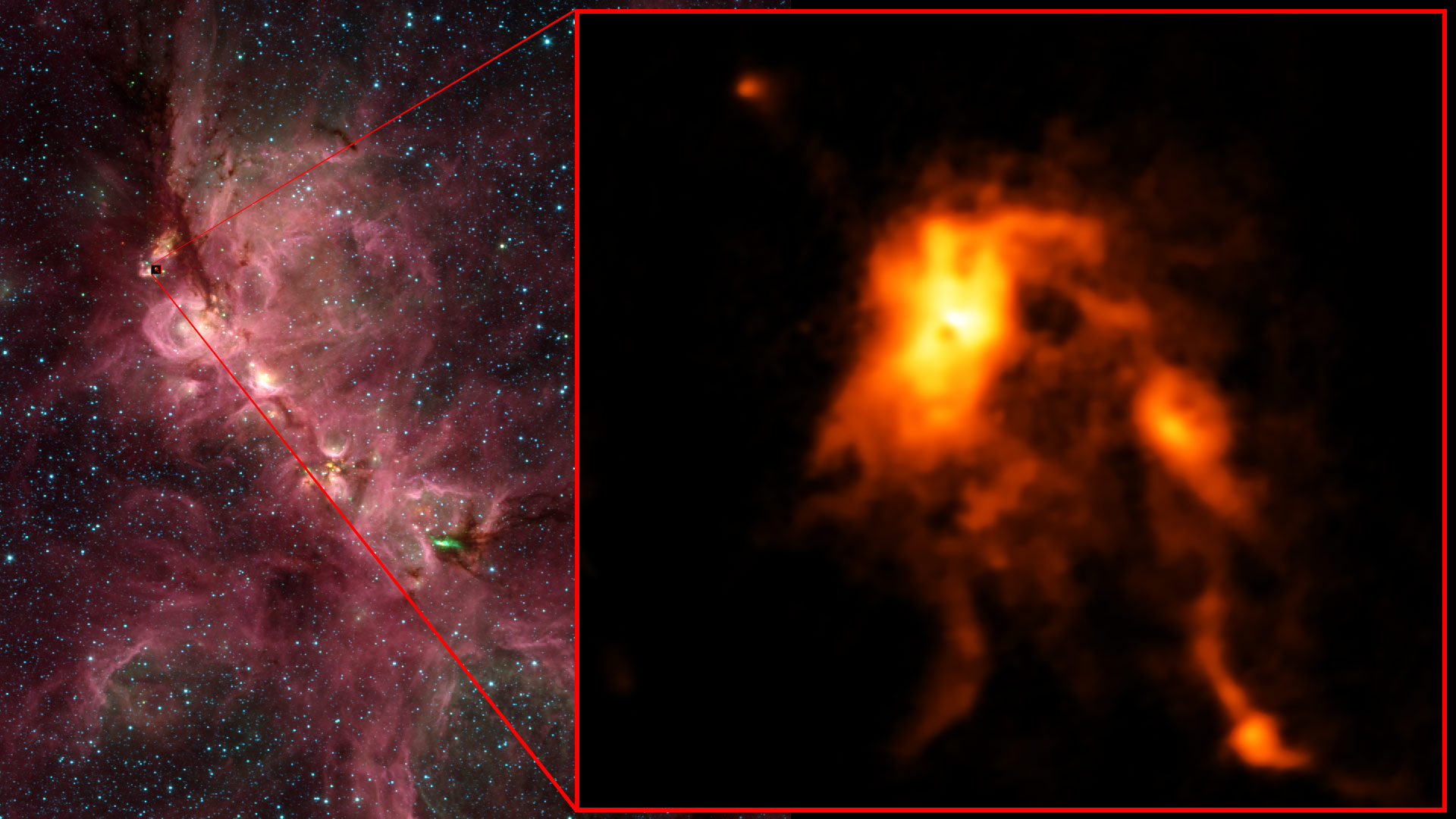

Protostar Blazes Bright Reshaping Its Stellar Nursery National Radio Astronomy Observatory

This Is A Classic Example Of A Reflection Nebula Where The Reflected Light From Young Hot Stars Illuminates A Protostellar Cloud Of Gas And Dust Universe Today

The Science Of Radio Astronomy National Radio Astronomy Observatory
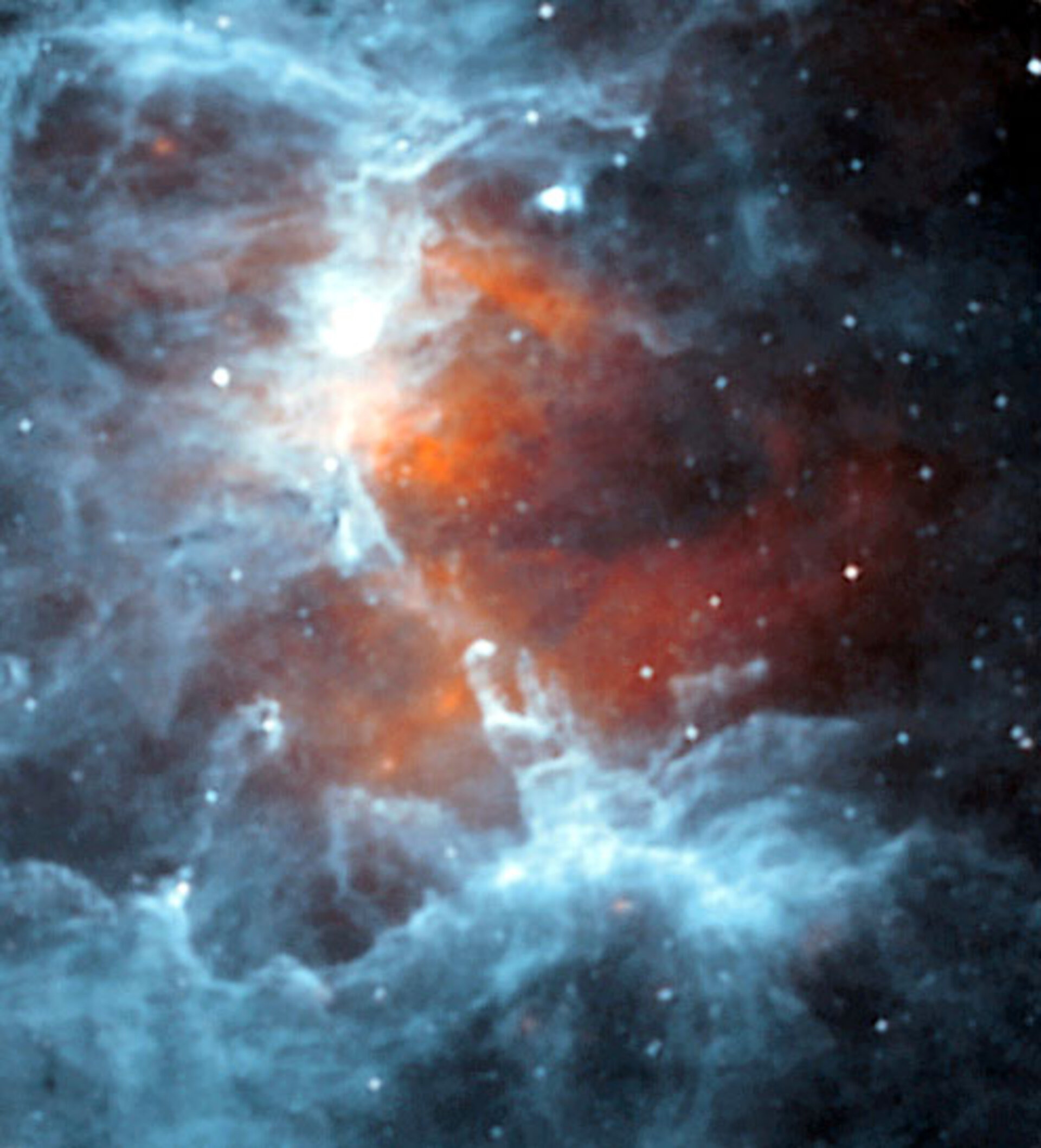

Esa Why Infrared Astronomy Is A Hot Topic
The Birth Of A Monster Star Seen At Different Wavelengths Of Light Eso

Nasa S Hubble Sees A Cosmic Caterpillar Hubble Telescope Space Telescope Hubble Space Telescope
Multi Wavelength Images Help Astronomers Study Star Birth Death Illinois
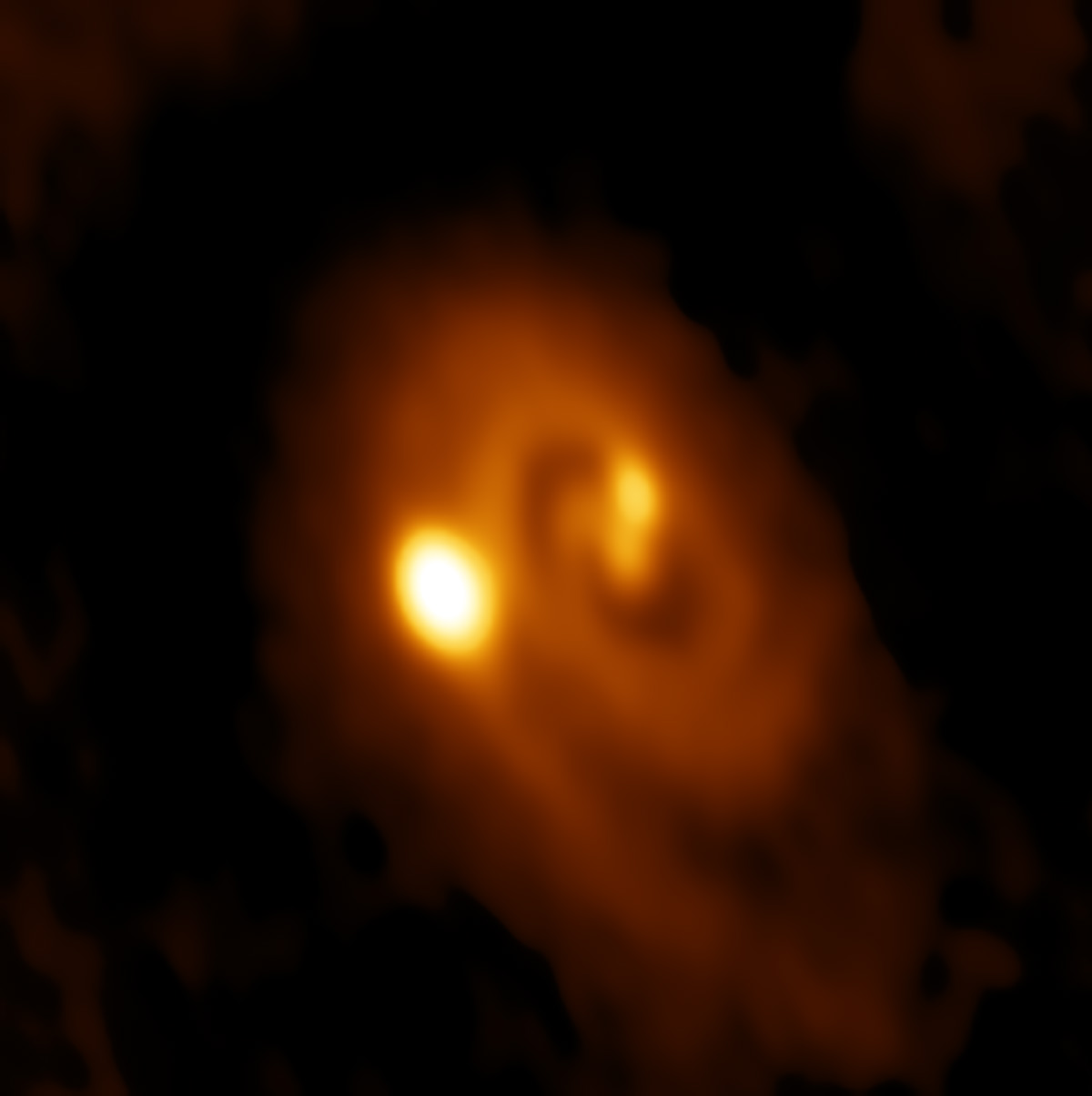

Astronomy Picture Of The Day December 2 2016 Star System Astronomy Space And Astronomy

Nasa Staff Shared Their Favorite Hubble Photos For The Telescope S 30th Anniversary Nebulosa De Orion Nebulosas Fotos De Universo


Comments
Post a Comment